Study Identifies Skin Microbe Link to Eczema Itching: Potential for New Treatments
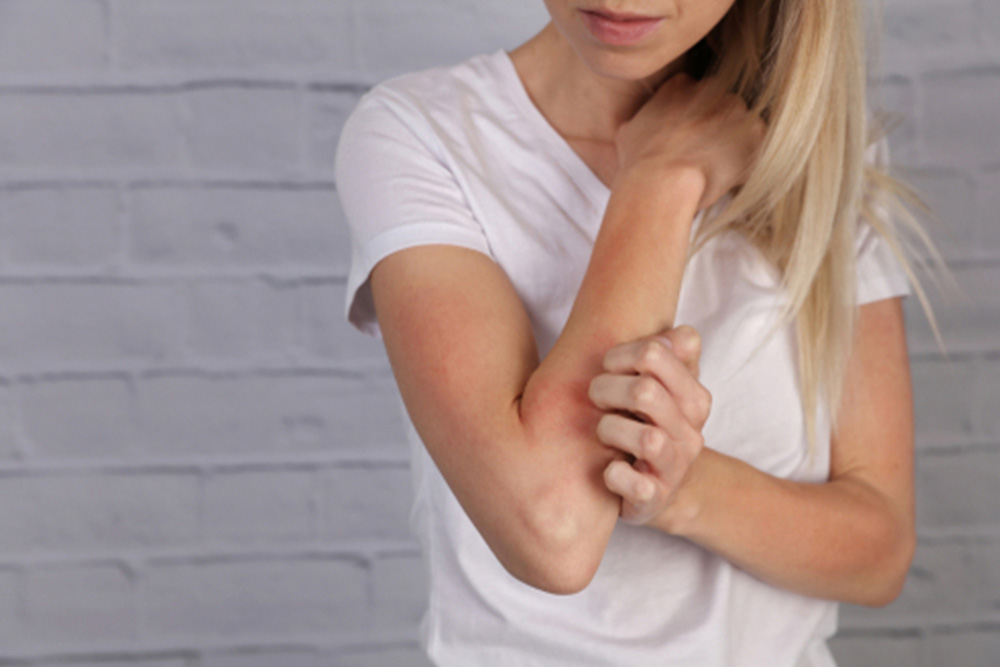

Eczema affects millions globally, with itch being a prominent symptom that impacts quality of life. Recent research investigated a potential link between eczema and oral microbiota, finding poorer oral health and altered microbial diversity in patients with eczema compared with controls. This highlights the need for increased awareness and potential therapeutic interventions for oral health issues in those with eczema.
Brain Natriuretic Peptide’s Role in Atopic Dermatitis Development
Researchers at North Carolina State University have made a significant discovery in understanding the role of a specific peptide in the development of atopic dermatitis (AD), commonly known as eczema. The research team focused on the brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), a short chain of amino acids found in higher levels in patients with AD. BNP is expressed in sensory neurons, which are crucial for conveying itch sensations to the brain. In a mouse model of AD, the absence of BNP resulted in a noticeable reduction in the typical skin thickening and irritation associated with AD, as well as decreased itching.
Study Shows Climate Change’s Impact on Atopic Dermatitis, Urges In-depth Research and Dermatological Action

A literature review conducted on climate change and atopic dermatitis (AD) reveals that climate change significantly affects atopic dermatitis (AD), influencing its prevalence, severity, and healthcare needs. The study examines the impact of ten climatic hazards and finds a mixed, but generally negative, impact on AD across different regions. The review, involving a multidisciplinary team, underscores the inconsistency of climate impacts on AD, with some areas like South Korea and the United States showing increased AD cases related to climatic events, while other studies show no clear link.
UV Phototherapy for Patients With Psoriasis and Eczema Does Not Increase Skin Cancer Risk
Researchers of a study aimed to determine if ultraviolet (UV) treatment, known to increase skin cancer risk due to excessive sun exposure, posed a similar threat in patients with psoriasis and eczema when used therapeutically. The study involved 3,506 patients treated with broadband-ultraviolet-B (UVB), narrowband-UVB, and/or combined ultraviolet A and broadband-UVB (UVAB) phototherapy, excluding treatments with psoralens. Over the course of the study, 79 patients were diagnosed with skin cancers, including melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma.
Guidelines for Atopic Dermatitis Management: Topical Treatments and Phototherapy

The American Academy of Dermatology recommends managing atopic dermatitis with emollients, soap-free cleansers, topical corticosteroids for flare-ups, and topical calcineurin inhibitors like pimecrolimus and tacrolimus. While ultraviolet phototherapy is effective for more severe cases and antistaphylococcal antibiotics can treat secondary infections, oral antihistamines and integrative medicine lack evidence of effectiveness.
Study Finds Vitamin D in Pregnancy Lowers Eczema Risk in Babies and Improves Bone Density
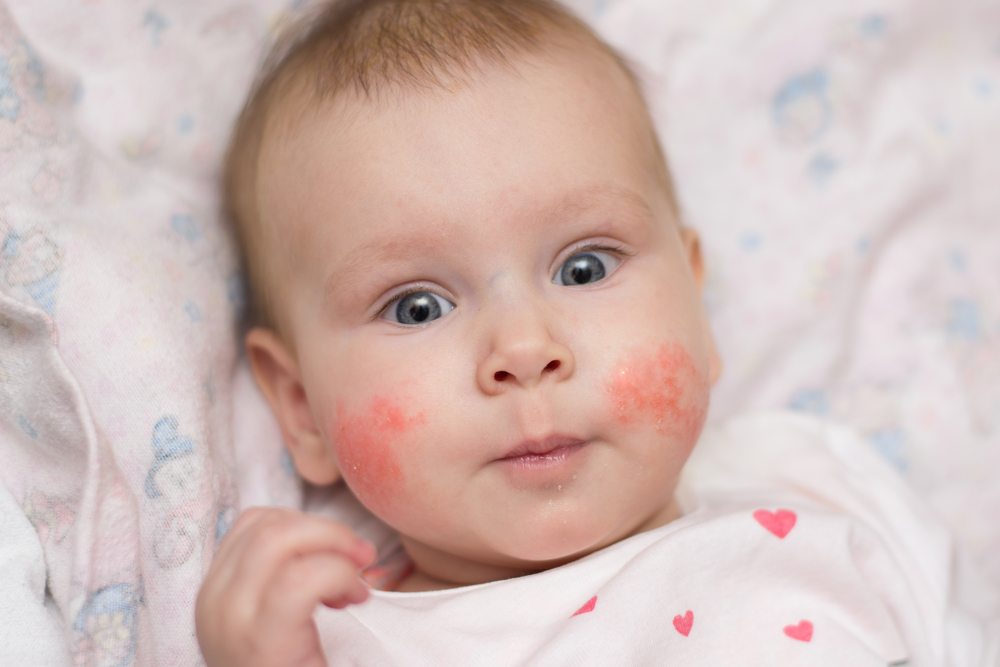

A University of Southampton study indicates that vitamin D supplements during pregnancy may reduce eczema risk in children at 12 months, with the effect lessening at 24 and 48 months. Involving over 700 pregnant women, the study also found that these supplements can improve the child’s bone density at 4 years old, as part of the Maternal Vitamin D Osteoporosis Study.

